Thursday, November 25, 2010
Java Engine Administration Tools

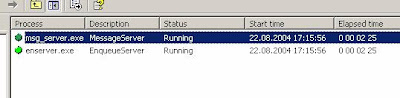
Logfiles Startup J2EE Instance

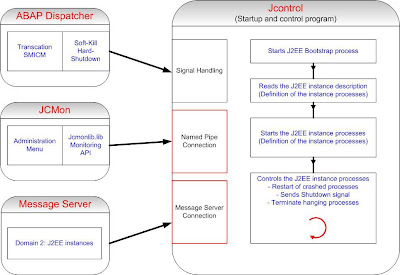
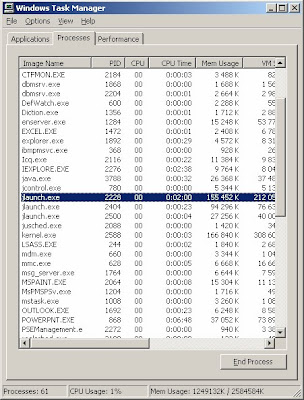
JControl and JLaunch
Wednesday, November 24, 2010
JCMon – Monitor Program
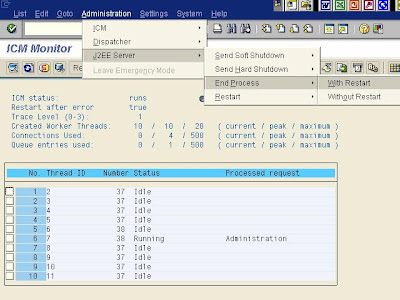
Start/Stop of Java Engine processes in ICM Monitor
Starting and Stopping SAP with scripts (UNIX & Windows)
J2EE Startup Framework
Monday, November 1, 2010
J2EE Engine - Profile Parameters
Exe/j2ee full path to JControl
rdisp/j2ee_error Number of incorrect attempts to start a J2EE Engine before the restart is deactivated.
rdisp/j2ee_start Activates or deactivates starting the J2EE Engine.
rdisp/j2ee_start_lazy
- If 1 and if the rdisp/j2ee_start is set - the J2EE Engine it is not started until the ABAP runtime environment has been fully initialized. This avoids problems that are caused by a long initialization phase.
- If 0 (default) – the J2EE Engine can be started without waiting for the ABAP initialization.
rdisp/j2ee_timeout Time span, the J2EE Engine must log on to the Web Dispatcher.
SDM Instance

Software Deployment Manager (SDM)
SDM Server
started automatically as part of WEB AS 6.40
one SDM Server per WEB AS 6.40 with J2EE Engine is necessary
SDM Interfaces
1) Commandline Interface (sdm.bat or sdm.sh)
(b) No SDM Server may run at the same time (this is checked).
2) JAVA API (SDMclient.sda) needs a running SDM Server
3) SDM Gui (sdmgui.bat or sdmgui.sh) needs a running SDM Server
- Another special instance is the one that installed the SDM (Software Deployment Manager). This one usually runs with the database and Central Services on the same machine and is then indicated as the central instance.
- The Software Deployment Manager (SDM) is a tool with which you can manage and deploy software packages that you receive from SAP or created with NetWeaver Developer Studio.
- The Software Deployment Manager (SDM) groups several different deployment types in a single network interface for the deployment of any software that you develop with the SAP NetWeaver Developer Studio.
- In all modes SDM is only able to handle one access at a time.
Java Instance – Server Process

Server Process components:
Connection request handler receives the first request from a client. From this time point on, the client has a fixed connection to the dispatcher.
Session level services are services that are assigned to a session.
Application-level services or the actual application program.
1) The Server Processes of the J2EE Engine actually execute the J2EE application.
Each server process is multi-threaded, and can therefore process a large number of requests simultaneously. Java Dispatcher assigns requests to the server processes.
2) The identification of the jlaunch processes can be easy done with their PID, the PID is also represented in the monitoring tools as the SAP Management Console.
Java Instance – Java Dispatcher
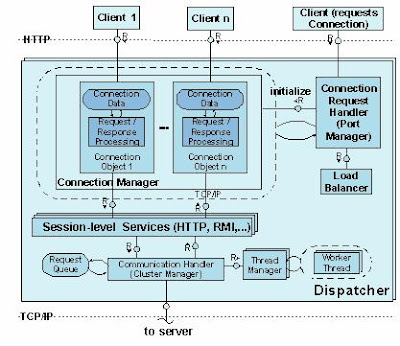
Java Dispatcher components:
Connection request handler receives the first request from a client. From this time point on, the client has a fixed connection to the dispatcher.
Connection manager manages the existing connections to the clients.
Session level services are services that are assigned to a session.
Communication handler forwards the request to the server process.
Accumulating requests are stored in the request queue.
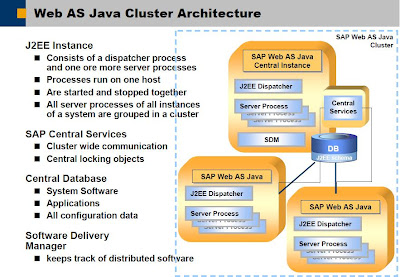
1) A Java instance is a unit in the SAP Web Java cluster, which can be started, stopped, and monitored separately. It runs on a physical server; but it is also possible to run several instances on one server. An instance is identified by the system ID (SID) and the instance number.
2) One Java instance contains at least one Dispatcher and one Server Process, the Central Services (Message, Enqueue) and the SDM.
3) A Java instance is started and stopped by the Java Startup and Control Framework.
4) The Java dispatcher receives the client request and forwards it to the server process with the lowest capacity usage. If there is already a connection to the client, the request goes to the server process that processes this client.
5) Dispatcher processes are represented by a jlaunch processes
6) The Java Dispatchers do not communicate to each other, they are light applications used for load balancing to the local servers only.
7) Interprocess communication Dispatcher on one box – Server on other box is not possible.
Locking Adapter in the Visual Administrator

With the Locking Adapter checks and tests of the Enqueue Service can be done.
The locking adapter service establishes the interface between the J2EE Engine and the enqueue service.
You can display and manage locks, carry out tests, and display statistics.
The locking adapter service is available on each server process, but it is not available on the dispatcher. It connects to the Enqueue Service and fetches requested data or sends changed data to it. As there is only one enqueue server in the system, all the locking services of the various server processes have the same information. Therefore it is not important on which
server process you use the locking adapter service.
Locks are used for example during deployment of applications. The configuration manager requests a lock from the Locking Manager. The Locking Manager in turn requests the lock from the Enqueue Service. The relevant area in the database is locked
To look into the Locking Adapter use the following path:
1. Start the SAP J2EE Engine visual administrator.
2. Choose Cluster -> Server 0 -> Services
3. Choose Locking Adapter
Choose the Runtime tab page to see a list of the functions offered in the locking adapter service:
To display existing locks; choose Display Locks.
To set and release locks, choose Create/Release Lock.
To delete existing locks, select the locks and choose Delete Selected Locks.
To run test programs, choose Run Tests. To run functional tests choose Execute Functional Tests, and to load tests choose Execute Load Tests).
To display files, choose View Files. You can view the profile data or the trace file of the lowest layer of the enqueue service. This is useful for looking for errors.
To display statistics, choose Time Statistics.
Thursday, October 21, 2010
Central Service - Enqueue Service

- The Enqueue service runs on the Central Services instance of the Java cluster. It manages the lock table in the main memory and receives requests for setting or releasing locks.
- It also maps the logical locks to the database.
- The Enqueue service can be configured for high availability, by setting it up with the replication server and a platform-independent high availability solution.
- The status of the Enqueue service are made accessible to the administrator via the Locking Adapter Service in the Visual Administrator.
- The terms Enqueue server and Enqueue service are used synonymously. The correct expression is that the Enqueue server is the program or process that provides the Enqueue service.
- Enqueue Service is represented by an en.sap
process
Message Info Service in the Visual Administrator

- The message info service is the interface between the J2EE Engine and the Message Service, it is used it to monitor and administrate the message server.
- The message service doesn’t communicate direct to the Message Server, but it is using the cluster manager, which has a direct connection to the message server.
- The message info service is not automatically started when the J2EE Engine is started.
Web AS Java Cluster Architecture
Monday, March 8, 2010
Activating the Emergency User SAP* in AS Java
a. Start the config tool.
b. Set the following UME properties:
| Property | Value | Comment |
| ume.superadmin.activated | true | This activates the SAP* user. |
| ume.superadmin.password | <password> | Enter any password of your choice. This defines the password for the SAP* user. |
Log on to identity management to unlock users or create a new administrator user.
a. Start the config tool.
b. Set the property ume.superadmin.activated to false.